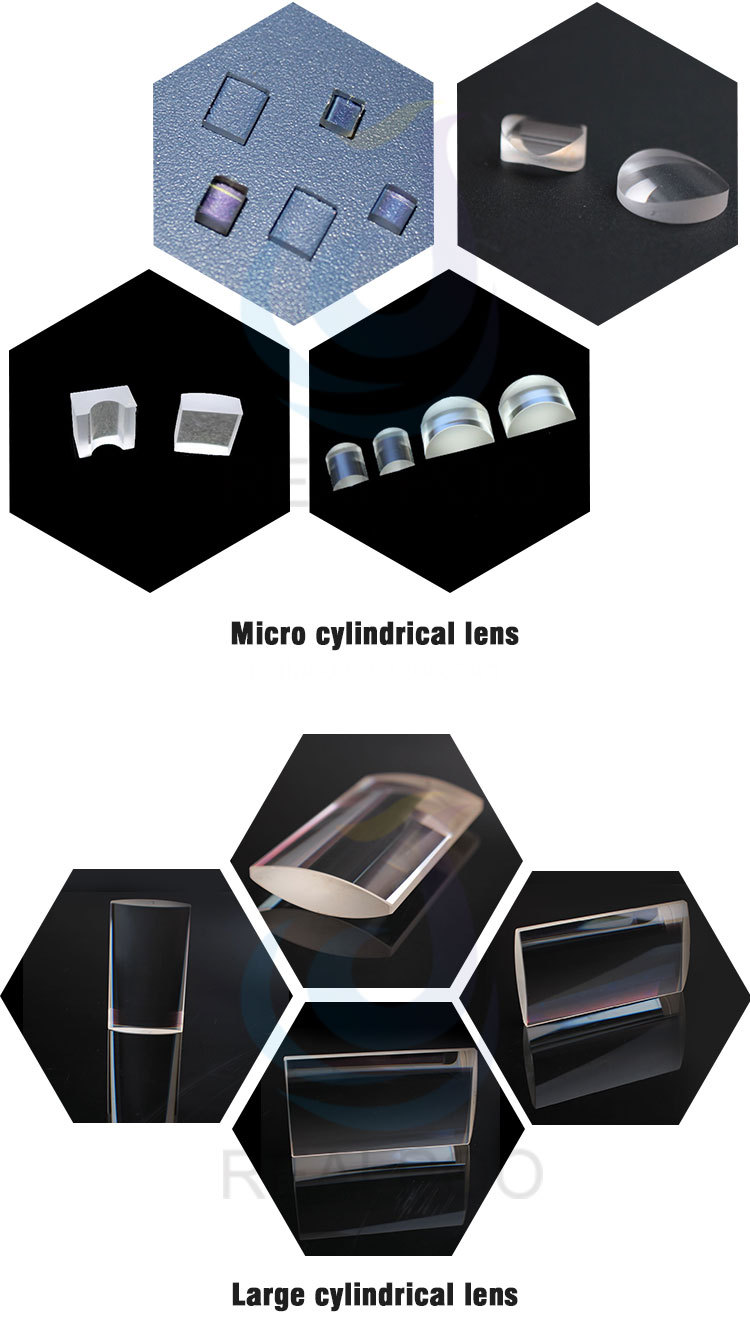
Cylindrical lens are offered in both plano-concave and plano-convex configurations, they are typically used to focus incoming light to a line, or to change the aspect ratio of an image. Cylinder Lenses are available with positive or negative focal lengths, they are used for the optics, lasers, medical science, electronics, tele-communication and others.
Cylindrical lenses,Positive cylindrical lenses, Line Light,Laser Focusing Lenses,Negtive cylindrical lenses Changchun Realpoo Photoelectric Co., Ltd. , https://www.optics-realpoo.com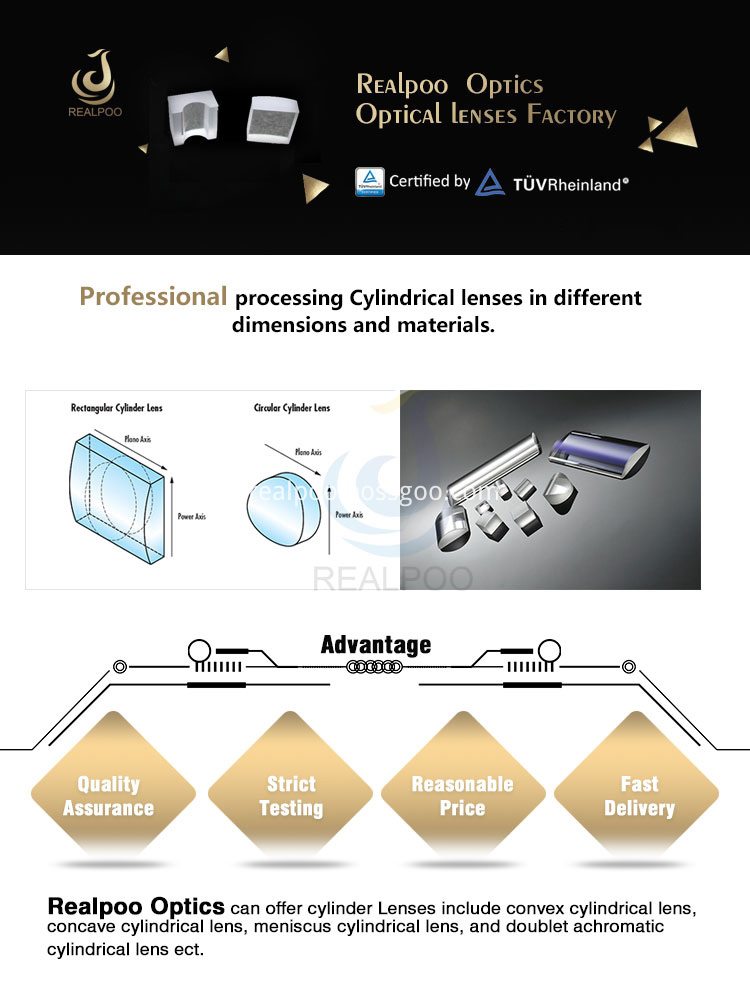




China's power battery pattern: 70% or will dominate the $240 billion global battery industry
The tech-detail-main section features a detailed product display with a sliding image gallery and thumbnails. Each image is accompanied by a description, highlighting key components such as "Car Audio Crystal 3.2*2.5mm 3225 24M (24.000MHZ) 20PF 10PPM 20PPM 30PPM," "ESD TVS electrostatic protection tube 0201 package 3.3V ultra low capacitance ESD," "inductance," and "SMD aluminum electrolytic capacitor." This visual presentation gives users a clear view of the product’s technical specifications and quality.
Even those who believe they have a solid understanding of the electric vehicle industry may only be familiar with a handful of major power battery suppliers. Names like Panasonic from Japan, Samsung from South Korea, LG Chem, Tesla, and China’s leading automaker BYD often come to mind. However, when presented with a broader list of battery manufacturers, many might be surprised to learn that China alone has over 140 battery companies actively expanding their production capacity. These firms are vying for a share in an industry projected to be worth $240 billion over the next two decades.
With the global automotive industry once driving massive economic growth, the rise of electric vehicles and batteries could create a similar boom in China. The country is already making significant strides in this sector, aiming to dominate the global battery market in the years to come.
According to research by Bernstein Automotive, electric vehicles are expected to make up 40% of global car sales within the next 20 years. If current trends continue, annual EV sales could reach 40 million units, with batteries accounting for a large portion of the value. Assuming an average battery cost of around $6,000—comparable to a traditional internal combustion engine—the battery industry could grow to a staggering $240 billion.
China has been aggressively pushing for cleaner energy and reducing air pollution, which has accelerated its focus on electric vehicles and battery technology. This strategic move positions the country as a leader in the global battery race.
To meet rising demand, battery production must expand significantly. This is why Chinese manufacturers are rapidly scaling up their operations. In 2014, Tesla and Panasonic launched what many called a "battery arms race" after announcing plans for a massive super battery factory.
China's battery production is growing at an astonishing pace, with its share of global output surpassing that of Japan and South Korea. By 2020, it was estimated that China would account for over 70% of global battery production. This rapid growth is fueled by both the booming electric vehicle market and the preference of Chinese automakers for domestic battery suppliers.
According to the second-quarter 2017 report from Roland Berger’s Electric Vehicle Index, more than 90% of lithium-ion batteries used in Chinese electric vehicles were made domestically. As the industry expands, the government is stepping in to regulate and consolidate its position as a global leader.
In 2016, a draft guideline was issued requiring battery manufacturers to have at least 8 GWh of production capacity to qualify for funding. Later, the government signaled its intention to further narrow support, offering subsidies only to companies producing over 40 GWh annually.
Despite competition from global giants like Panasonic, Chinese companies are catching up quickly. Shenzhen-based BYD, for example, produced nearly 500,000 electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles in 2016, with a battery production capacity of 20 GWh. Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway invested $230 million in BYD in 2008, securing a 10% stake. Today, BYD’s market value stands at $16.9 billion.
Another major player is CATL (Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited), founded in 2011 and based in Ningde, Fujian. Specializing in lithium-ion batteries and energy storage systems, CATL has expanded rapidly, with a current capacity of 7.7 GWh and plans to reach 50 GWh by 2020. The company is also a key target for government support.
In the Chinese battery market, companies like BYD, CATL, Guoxuan Hi-Tech, and others are leading the charge. According to 2016 global power battery sales rankings, seven of the top ten companies were Chinese, including BYD, CATL, Waterma, Guoxuan Hi-Tech, Lishen, BAK, and AVIC Lithium. Wanxiang A123 and Harbin Optics also ranked among the top 15.
Lishen, for instance, operates production bases in multiple cities and aims to reach 20 GWh by 2020. Wanxiang, one of China’s largest private companies, has made several acquisitions, including A123 Systems and Fisker Automotive, further strengthening its presence in the global battery industry.
While the shift to electric vehicles promises immense growth for the battery industry, it also signals the decline of traditional internal combustion engines. As more EVs hit the road, the demand for batteries will surge, while the need for conventional engines will diminish. This transition marks a turning point in the automotive world, with China at the forefront of the revolution.