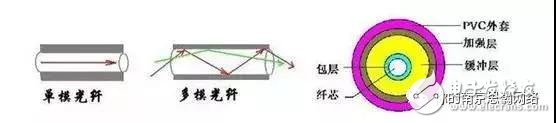
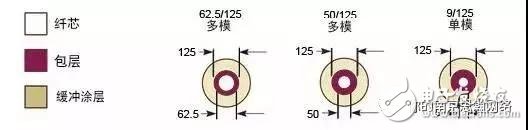
With the growing demands for high-speed and reliable communication, optical fiber has become the preferred choice for data transmission due to its fast speed, long-distance capability, safety, stability, and resistance to interference. In intelligent building projects, long-distance data transfer is common, and fiber optics are often the go-to solution. However, many users find it confusing to distinguish between single-mode and multi-mode fibers. This article will explain the key differences between the two in a clear and straightforward way. Both single-mode and multi-mode fibers are designed for high-quality long-distance data transmission, but their methods of light propagation differ. In single-mode fiber, light travels in a straight line without reflecting, allowing it to cover much greater distances. Multi-mode fiber, on the other hand, allows multiple light paths (modes) to travel through the core, making it suitable for shorter distances but more cost-effective. Single-mode fiber has a very small core diameter, typically between 8.3μm and 10μm, and supports only one mode of light transmission. This results in higher bandwidth and faster data rates compared to multi-mode fiber. However, it requires a more precise light source with narrow spectral width and high stability. Due to these characteristics, single-mode fiber can transmit data over much longer distances—up to 50 times farther than multi-mode fiber—and is generally more expensive. The smaller core size and single-mode operation help prevent signal distortion caused by overlapping light pulses. As a result, single-mode fiber experiences the lowest signal loss and offers the highest transmission speeds among all fiber types. Multi-mode fiber has a larger core diameter, usually ranging from 50μm to 100μm, which allows multiple light modes to travel simultaneously. This makes it ideal for short to medium-range communications. In Ethernet applications like 10Mbps or 100Mbps, multi-mode fiber can support distances up to 2000 meters. Common core sizes include 50μm, 62.5μm, and 100μm. However, because multiple modes are transmitted, each with different propagation speeds, this leads to modal dispersion, limiting the bandwidth and increasing signal loss. Therefore, multi-mode fiber is best suited for local area networks (LANs) and systems that require lower capacity and shorter distances. In real-world applications, single-mode fiber is typically used when the transmission distance is long, while multi-mode fiber is more commonly used for shorter links. Additionally, the transceivers used with single-mode fiber tend to be more expensive than those for multi-mode fiber. One of the easiest ways to tell the difference between single-mode and multi-mode fiber is by examining the core and cladding diameters. Industry standards have been established to guide the selection of fiber optic connectors, splices, and tools, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance in various network setups. Single Phase Voltmeter,Led Single Phase Voltmeter,Voltage Measurement Tool,Digital Voltmeter zhejiangjinyidianqiyouxiangongsi , https://www.jooeei.com