This article refers to the address: http://
HDTV (High Definition Television) can play high-definition video programs such as DVDs for TV users. At the same time, these HDTVs also begin to integrate Internet video and image playback functions, but these video images often contain a lot of noise, which is in HDTV. Very obvious. In addition, most TV shows are still SD, which relies on high-quality scaling and resolution enhancement algorithms to achieve high-definition images. To solve this problem, IDT's HQV Vida processor combines two new IDT HQV technologies, namely automatic HQV and HQV StreamClean, which are two new technologies that automatically improve the quality of video images and provide powerful source video cleanup capabilities. The noise in the image, while enhancing the image resolution, can provide TV users with as clear and clean HD TV effect images as possible.
1 There are three types of noise commonly found in noise video in video images : random noise, block noise, and mosquito noise. Random noise is often found in analog video and also in video captured with a noise sensor or in low light conditions. Block noise and mosquito noise occur mainly due to excessive compression of digital video. In its non-fully compressed state, Full HD video has a bandwidth of approximately 3.7 Gb/s, while SD video has approximately 620 Mb/s of bandwidth, both of which have large bandwidths and are not suitable for transmission. In order to solve this problem, an MPEG compression algorithm is usually used, which is very powerful and can reduce the bandwidth to a small extent without causing significant image quality degradation. In general, HD can be compressed to 9 Mb/s, or SD can be compressed to 4 Mb/s without significant impact on quality, but with block noise and mosquito noise distortion. A large amount of video content can now be viewed on HDTV via the Internet, but many Internet connections are less than 1 Mb/s bandwidth peak, far below the 4 Mb/s continuous bandwidth required to achieve high quality SD programming, which is Internet video usually has a lot of block noise and mosquito noise. Since the MPEG algorithm splits the image before compression, a block is generated. When the degree of compression is too high, some information of the block is lost, and the reconstructed image will have a boundary; when the video contains fast moving content, this phenomenon is especially obvious. Mosquito noise occurs when the bit rate is too low and the mathematical compression algorithm does not have enough information to reconstruct the original image. Mosquito noise is a very slender noise that often appears on the edges of objects with a flat background, such as around a person's silhouette.
2 HQV Vida Processor Noise Reduction and Resolution Enhancement IDT's HQV video processing technology utilizes true 1080i to 1080p HD deinterlacing and an advanced multi-directional diagonal filter that ensures video without jagged edges for the sharpest and sharpest HD images. The HQVVida processor includes powerful algorithms to remove block noise and mosquito noise distortion. It can detect borders and mosquito noise in any image, even those that were previously scaled. The HQV Vida processor only corrects the boundaries, reduces block distortion, and performs adaptive mosquito noise reduction in the noise region to clean the image while preserving image detail. 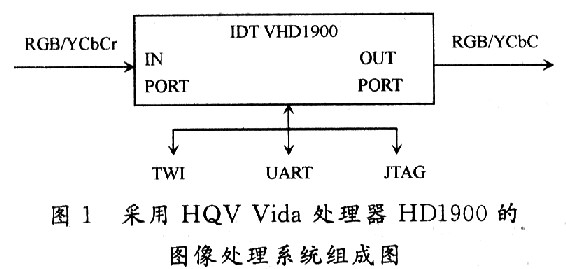
Figure 1 shows the composition of the image processing system using the HQV Vida processor HDl900. The system is powerful but simple in structure. In addition to the input and output ports, there are only TWI bus interfaces and UART and JTAG interfaces. The HDl900 integrates the new HQV and HQV StrearmClean technologies into the chip. The HQV StreamClean incorporates adaptive mosquito noise, mosaic and time-three noise reduction techniques to selectively reduce these difficult image distortions. At the same time, automatic HQV technology enables manual-free adjustment to optimize image quality from different sources or content of varying quality.
The HDl900 features 14-bit internal processing and 12-bit 3D color gamut conversion for color depth output processing and xvYCC processing, which accurately translates normal and wide color gamut content into the display's native color gamut. The VHDl900 also features 6-axis color control that independently adjusts the hue, saturation and brightness of any color. All video processing technologies are fully integrated and manufactured to the smallest size of existing video processors. The HDl900 video processor eliminates the need for external memory and can be easily integrated into any video system by integrating on-chip memory.
The HDl900 image processor is able to determine random noise so that it is not confused with small moving elements such as rain, fog or smoke in the image. These can be implemented by the HQV Vida processor by tracking the moving elements on several frames to see if they have a reasonable motion vector, and those elements that do not have a random motion pattern can be eliminated as noise. These noise reduction processes are adaptable because they only apply to noise pixels in the image.
3 HQV Vida processor resolution enhancement Most video content now uses SD resolution, and a lot of Internet content even uses lower resolution. In order to convert these video sources into high definition formats, a high quality scaling engine is required. Although these images have the same pixels as the local HD material, the details are different, which requires the resolution enhancement engine of the HQV Vida processor. The HQV Vida processor utilizes four-field motion adaptive de-interlacing and multi-field tracking to enhance image detail and quality, extending 12-bit color processing and detail enhancement. By using a resolution enhancement algorithm, you can enhance it only on edges that need to be enhanced or not sharp enough, or in progressive areas of the image. Resolution enhancements can also be used for high-definition video, which turns the standard definition source into HD quality, making the details look sharper. In addition, the device provides real-time cleanup of highly compressed video, reducing compression distortion from mosaics and mosquito noise from low quality sources. By adaptively enhancing the edges of the image, the Vida algorithm can make up-converted SD material look close to HD material. Figure 2 shows the resolution enhancement effect of the HQV Vida image processor, where (a) is the original image, (b) is the effect of enhanced resolution, and the moss on the trunk is clearly visible. 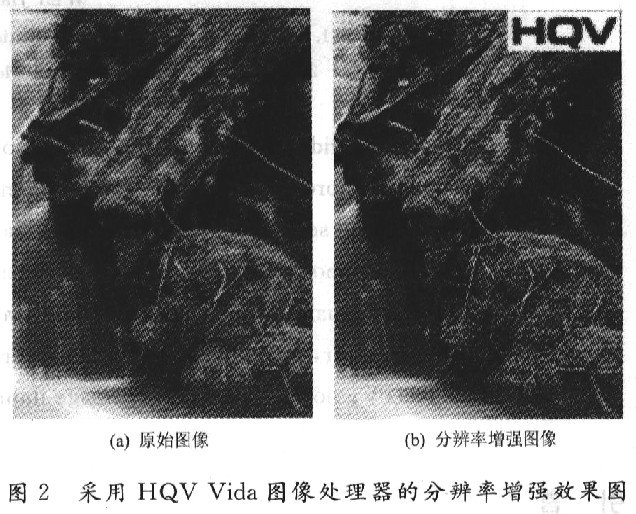
4 Conclusion HQV Vida processor uses powerful video processing technology to clean up the noise in high-compression, low-quality video broadcasting at any time, and can optimize the image quality of different quality and content from different sources or content, enhance the image display effect, so HQV Vida processor devices are ideal for DVDs, Blu-ray players, digital TVs, set-top boxes, personal audio recorders, audio and video receivers, projectors and mobile media device docks and media adapters.
HDTV image quality improvement based on HQV Vida processor
0 Preface